
 Select Route Tables from the left menu. We must create a route table for our public subnets to reach the internet via the internet gateway we created in the previous step. Elastic IP Allocation ID: Enter an existing Elastic IP or select Allocate Elastic IP address to allocate a new IP to your NAT gateway.Ĭreate a second NAT gateway but this time place it in the second public subnet, gitlab-public-10.0.2.0. Subnet: Select gitlab-public-10.0.0.0 from the dropdown list. Select Create NAT Gateway and complete the following:. Go to the VPC dashboard and select NAT Gateways in the left menu bar. To achieve this, we make use of NAT Gateways deployed in each of our public subnets: Instances deployed in our private subnets must connect to the internet for updates, but should not be reachable from the public internet. Select it from the table, and then under the Actions dropdown list chooseĬhoose gitlab-vpc from the list and hit Attach. Select Create internet gateway, give it the name gitlab-gateway and Select Internet Gateways from the left menu. Now, still on the same dashboard, go to Internet Gateways and Select each public subnet in turn, select Actions, and select Modify auto-assign IP settings. Once all the subnets are created, enable Auto-assign IPv4 for the two public subnets: Give it a descriptive name tag based on the IP,įor example gitlab-public-10.0.0.0, select the VPC we created previously, select an availability zone (we use us-west-2a),Īnd at the IPv4 CIDR block let's give it a 24 subnet 10.0.0.0/24:įollow the same steps to create all subnets: Name tag We create private and public subnets to match load balancers and This alsoĪllows us to enable multi AZ for redundancy. That each subnet is associated to the VPC we just created and Now, let's create some subnets in different Availability Zones. Select the VPC, select Actions, select Edit DNS resolution, and enable DNS resolution. If you don't require dedicated hardware, you can leave Select Your VPCs from the left menu and then select Create VPC.Īt the "Name tag" enter gitlab-vpc and at the "IPv4 CIDR block" enterġ0.0.0.0/16.
Select Route Tables from the left menu. We must create a route table for our public subnets to reach the internet via the internet gateway we created in the previous step. Elastic IP Allocation ID: Enter an existing Elastic IP or select Allocate Elastic IP address to allocate a new IP to your NAT gateway.Ĭreate a second NAT gateway but this time place it in the second public subnet, gitlab-public-10.0.2.0. Subnet: Select gitlab-public-10.0.0.0 from the dropdown list. Select Create NAT Gateway and complete the following:. Go to the VPC dashboard and select NAT Gateways in the left menu bar. To achieve this, we make use of NAT Gateways deployed in each of our public subnets: Instances deployed in our private subnets must connect to the internet for updates, but should not be reachable from the public internet. Select it from the table, and then under the Actions dropdown list chooseĬhoose gitlab-vpc from the list and hit Attach. Select Create internet gateway, give it the name gitlab-gateway and Select Internet Gateways from the left menu. Now, still on the same dashboard, go to Internet Gateways and Select each public subnet in turn, select Actions, and select Modify auto-assign IP settings. Once all the subnets are created, enable Auto-assign IPv4 for the two public subnets: Give it a descriptive name tag based on the IP,įor example gitlab-public-10.0.0.0, select the VPC we created previously, select an availability zone (we use us-west-2a),Īnd at the IPv4 CIDR block let's give it a 24 subnet 10.0.0.0/24:įollow the same steps to create all subnets: Name tag We create private and public subnets to match load balancers and This alsoĪllows us to enable multi AZ for redundancy. That each subnet is associated to the VPC we just created and Now, let's create some subnets in different Availability Zones. Select the VPC, select Actions, select Edit DNS resolution, and enable DNS resolution. If you don't require dedicated hardware, you can leave Select Your VPCs from the left menu and then select Create VPC.Īt the "Name tag" enter gitlab-vpc and at the "IPv4 CIDR block" enterġ0.0.0.0/16. 
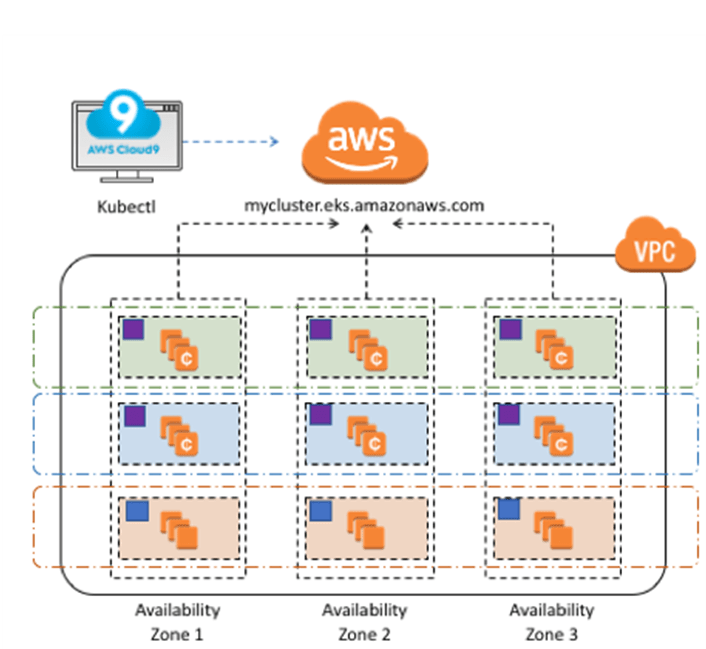
We now create a VPC, a virtual networking environment that you control: Public subnets require a Route Table keep and an associated We can create subnets to have public and private instances in at least We start by creating a VPC for our GitLab cloud infrastructure, then We use this role when we create a launch configuration later on.
Give the role a name (we use GitLabS3Access) and select Create Role. In the policy filter, search for the gl-s3-policy we created above, select it, and select Tags. Create a new role by selecting AWS service > EC2, then select. Still on the IAM dashboard, select Roles in the left menu, and. Select Review policy, give your policy a name (we use gl-s3-policy), and select Create policy.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
